What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
What does the PaaS acronym stand for?
The acronym PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. PaaS provides a complete development and deployment environment so developers can focus on building applications without having to worry about buying and managing the underlying hardware and software.
In other words, PaaS allows users to focus on their business model rather than having to worry about the technology infrastructure required to support it. These characteristics make it an attractive option for those businesses that want to rely on cloud computing but are daunted by the thought of having to manage their own IT infrastructure.
PaaS providers offer a variety of services. These include application hosting, development tools, database and storage services, and monitoring and management tools.
Typically, the offering is provided as a subscription service, with prices scaling with application requirements on a “pay as you go” basis.
However, PaaS is not unreservedly suitable for every use case. Applications that require a high level of customization or need to be explicitly provisioned for specific hardware or software platforms may be better suited to other delivery models such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or on-premises.
The differences between PaaS, IaaS and SaaS
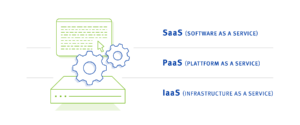
PaaS, IaaS and SaaS are all models of cloud computing. PaaS is a platform for developers to create and deploy applications.
IaaS is a set of infrastructure services that can be used to create and run applications. It includes a range of services such as storage, networks and computing power that can be used to build and run applications. IaaS providers:in generally charge by the hour or by the amount of resources used.
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a software application that is provided as a service. SaaS applications are usually accessed via a web browser. SaaS providers:inside usually charge a monthly or annual subscription fee.
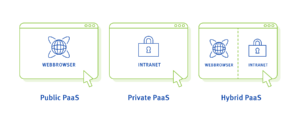
Public PaaS, Private PaaS, Hybrid PaaS
There are three different types of PaaS. Each type has its advantages, and it is important to decide which one is right for your needs.
Public PaaS are typically accessible through a web browser. This makes them ideal for companies that want to quickly develop and deploy applications without having to worry about setting up their own infrastructure.
Private PaaS, on the other hand, are offered by companies to their employees and are usually accessible via the company’s intranet. This makes them ideal for companies that use sensitive data or applications that they want to protect from the public.
Hybrid PaaS offer the best of both worlds, allowing companies to use public clouds for less sensitive applications and private clouds for more sensitive applications. This makes them ideal for companies that want the flexibility to decide which applications to deploy on which type of platform.
10 advantages of Platform as a Service
- lower costs: PaaS can help you save on infrastructure and middleware costs by eliminating the need to manage and maintain these components yourself.
- Increased efficiency: PaaS solutions are designed to be easy to use, which can save you time and effort when developing and deploying new applications.
- Faster time to market: by using a PaaS solution, you can get your applications up and running quickly without having to worry about configuring or managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Scalability: PaaS solutions are typically highly scalable, meaning you can easily increase or decrease your usage as needed.
- versatility: PaaS solutions offer a degree of flexibility, which can be helpful when you need to quickly deploy new applications or make changes to existing ones.
- compatibility: most applications are compatible with PaaS solutions, so you probably won’t need to rewrite your applications to work in this environment.
- ease of integration: PaaS solutions connect easily with other cloud-based services or on-premises systems, making it easy to get started.
- Comprehensive offerings: Many PaaS offerings consist of a complete suite of tools and services, making it easy to find all the services you need in one place.
- Support: Some PaaS providers provide 24/7 support to enable around-the-clock assistance.
- Free trials: There are often time-limited free trials offered to try out the service before you commit.
10 disadvantages of Platform as a Service
- lock-in to the provider: When you use a PaaS solution, you are usually dependent on the provider for both the platform and the infrastructure. This fact can make it difficult to switch providers or move to a different solution when needed.
- Less control: with PaaS, you often have less control over the underlying infrastructure than with an IaaS solution. This can make it difficult to customize the environment to your specific needs or to quickly troubleshoot any issues.
- Limited scalability: PaaS solutions are often designed for scalability. However, depending on the provider and the plan you choose, scalability may be limited up or down. This can become problematic if your needs change or go beyond the capabilities of the platform.
- increased costs: although PaaS offers cost savings compared to traditional deployment models, the costs can add up over time and offset the initial benefit.
- security concerns: because PaaS solutions abstract the underlying infrastructure, it can be more difficult to protect your applications and data from potential threats. This should be considered if security is a high priority for your business.
- Complexity: PaaS solutions can be complex, making them more difficult to use. This is especially true if you are unfamiliar with cloud computing or have limited experience with programming and development.
- Lack of flexibility: PaaS solutions are usually designed to provide some degree of flexibility. However, they may not be as flexible as some other delivery models.
- incompatibility: not all applications are compatible with PaaS solutions, which means you may need to modify your applications to make them work in the PaaS environment. Depending on the size and complexity of the applications, this can be a time-consuming and costly endeavor.
- Limited resources: depending on the provider, CPU, memory, storage, and other resources you can use for your applications may be limited. This can impact performance or the number of users using your applications.
- Downtime: As with any other service, PaaS solutions may experience downtime due to maintenance, updates, or unexpected issues. This can disrupt your business operations and lead to lost productivity if not managed properly.
Four Components of a Platform as a Service
There is no blanket answer to the question of which components make up a Platform as a Service, since providers offer a wide range of services. However, there are usually four core components that make up the platform. These components are:
Infrastructure: the infrastructure is the foundation of the platform and includes the hardware, operating system, storage, network and more.
Middleware: Middleware is the software that sits between the applications and the infrastructure. It includes the application server, database, web server and other components.
Applications: Applications are the software that runs on the platform. This includes web applications, mobile applications and more.
DevOps tools: DevOps tools are the tools used to manage the platform. These include monitoring tools, deployment tools, automation tools and more.
These four components form the platform to provide a complete solution for enterprises.
Structure of a PaaS solution
A PaaS solution typically consists of a platform provider and a service user. The platform provider is responsible for providing the platform as a service, while the service user is responsible for using the platform to develop and deploy applications.
Providers typically deploy the platform as a preconfigured virtual machine or container so that service users have an out-of-the-box development environment. Users can then take advantage of this environment to develop and test applications before deploying the applications in the production environment.
In addition to the platform, PaaS solutions often include additional services such as storage, monitoring and load balancing. These services can be used by customers:inside to improve the performance and scalability of their applications.
PaaS solutions are typically based on cloud computing platforms, meaning they can scale to meet the needs of any business. They also offer a variety of features, such as:
- automatic provisioning and scaling of resources
- integrated security features
- asset management
- application monitoring
- API access for automation
- support for multiple programming languages
- cross-platform compatibility
- freedom from infrastructure issues
- ease of use and short implementation timeframes
- scalability to meet the needs of any business
How do I choose the right PaaS provider?
There are a variety of PaaS providers and it is important that you choose the right provider for your business. There are a few things to consider when choosing a PaaS provider, such as:
Features: What features does the Platform as a Service offer? Make sure the offering includes all the features you need to build and deploy your applications.
Pricing: make sure the pricing of the offering is compatible with your budget.
Support: what kind of support does the PaaS provider offer? Make sure the provider offers the level of support you need.
Compliance: evaluate how the PaaS provider handles compliance requirements. Among other things, compliance with all requirements of the GDPR is essential for data storage and processing of European personal data.
Certifications: Check the number and validity of the provider’s various certifications. Compliance with certification requirements is essential to ensure that all security and data protection standards are met
Platform as a Service Summary
Many enterprises are looking for ways to move away from managing their own infrastructure to a platform that is managed by experts.
PaaS solutions are often delivered through a cloud computing platform that provides users:on-demand access to resources and applications. This type of delivery model offers several benefits, including scalability, cost efficiency and flexibility.
PaaS can be a very attractive option for organizations of any size looking to improve their application development and deployment processes. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the capabilities and limitations of each PaaS solution before committing to a vendor.
Links to related topics
Public Cloud, what does it mean? A brief summary →
What is SaaS? Software as a Service explained in detail →
Why hybrid cloud is the best choice of all cloud variants →
5 important considerations to find the best possible cloud storage →
Wikipedia post about software as a service →